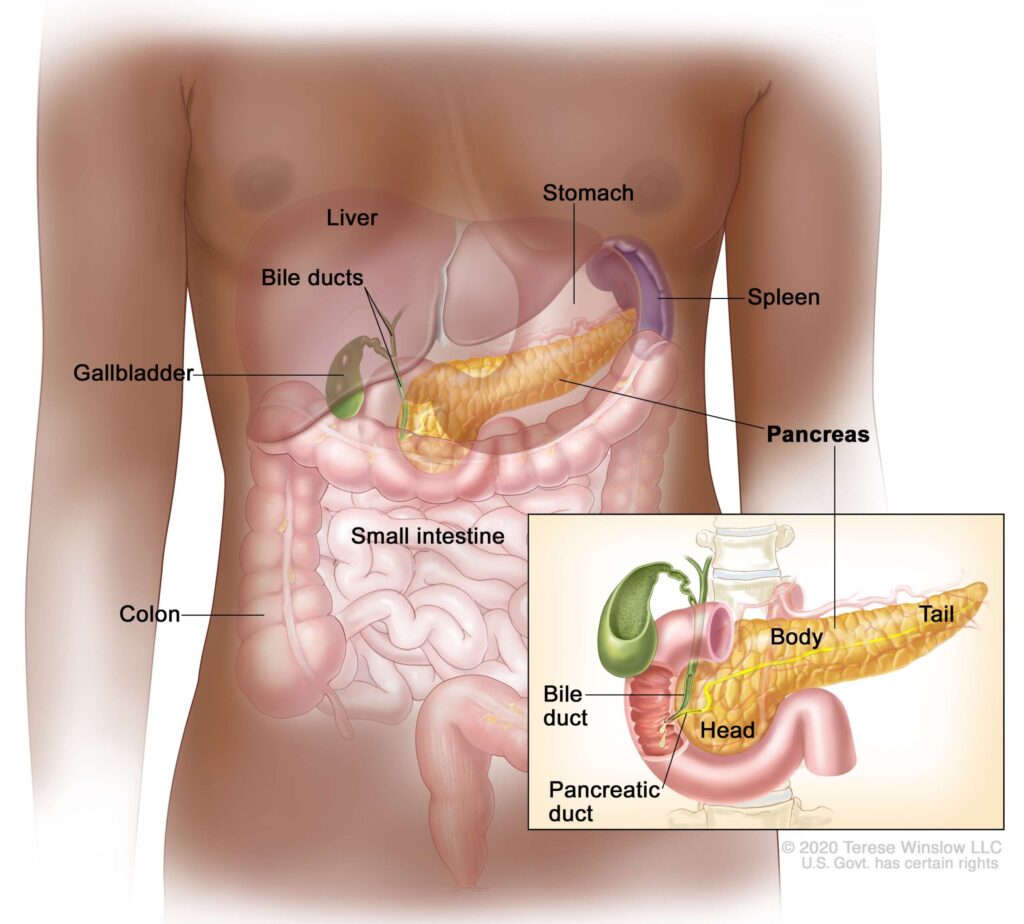
Staying active as you age is essential for maintaining your health, independence, and mental well-being. Here’s a quick guide to help you get started:
- Gentle Exercise: Begin with low-impact activities like walking, swimming, or cycling. Start small and build up gradually.
- Flexibility: Stretch regularly to reduce stiffness and improve mobility. Simple stretches like neck tilts and calf stretches can help.
- Strength Building: Use light weights or household items to perform basic exercises like chair squats and wall push-ups.
- Group Activities: Join local exercise groups or start your own. Walking clubs, aerobics, or church-based fitness sessions are great options.
- Digital Tools: Use apps like DrDoGood’s app or USSD services (_920_336#) to track your activity, set goals, and stay motivated.
Key Tip: Aim for 150 minutes of moderate activity weekly. Always consult your doctor before starting a new routine, especially if you have health conditions.
Staying active supports both body and mind but you have to remain mindful of your co-morbidities- start small and stay consistent.
5 Exercises Seniors Should Do Everyday
1. Start With Gentle Exercise
Starting with light exercise helps maintain mobility and independence. Studies show that active older adults experience 44.4% functional disability compared to 58.6% in less active peers. This highlights the value of incorporating low-impact workouts into your routine.
Best Low-Impact Workouts
Walking is a simple yet powerful option for older adults. Regular walking has been shown to lower functional disability by 67%, even among those with chronic conditions.
Here are some great low-impact exercises to try:
- Daily Walking: Start with 10–15 minutes and gradually increase to 30 minutes. Make sure you’re wearing appropriate shoes to reduce the risk of falls.
- Swimming: A great way to improve heart health without putting stress on your joints. If you don’t know how to swim, you can join or start a water aerobics group with a qualified swim instructor.
- Cycling: Delivers aerobic benefits while being gentle on your knees and hips.
These activities can easily fit into your lifestyle and support healthy aging.
Exercise Spots in Ghana
Ghana offers excellent facilities to support these activities. For example:
- Aviation Social Centre: Located in Accra, this facility features a gym, basketball courts, and spaces for social events. It also offers training programmes like aerobics, total fitness, kickboxing, boot camp, and body sculpting.
- Fitzone Ghana: Also in Accra, Fitzone provides fitness programmes, sports activities, and leisure options. They even run a cycling club in collaboration with Decathlon Ghana.
These locations make it easier to stay active and enjoy the benefits of regular exercise.
2. Keep Your Body Flexible
After adding gentle exercise to your routine, the next step is to work on flexibility. As we age, our joints can become stiff, and muscles may lose their elasticity. Physical therapist Kristin Vinci explains:
“If you start moving less as a result, your flexibility and mobility will also start to decrease. It’s a case of ‘use it or lose it.’”
Daily Stretching Guide
Stretching regularly helps maintain mobility and reduce joint stiffness. Aim to do these stretches at least three times a week:
| Stretch Type | How to Perform | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Seated Trap Stretch | Sit upright, grip the side of a chair with one hand, and tilt your head away. | Eases neck and shoulder tension |
| Standing Calf Stretch | Stand facing a wall, step one leg back, and press your heel into the floor. | Boosts ankle mobility |
| Seated Hip Flexor | Sit on a chair, let one leg drop off the side, and stretch it backward. | Improves hip flexibility |
| Seated Cat Cow | Sit with hands clasped behind your head; alternate rounding and arching back. | Enhances spine mobility |
Dr. Vinci offers this advice:
“Stretching is not a ‘no-pain, no-gain’ phenomenon. You don’t have to push into a deep, deep stretch or feel pain or discomfort for it to be beneficial.”
Tips for Effective Stretching:
- Hold each stretch for 10–30 seconds and repeat 3–4 times.
- Breathe steadily and avoid holding your breath.
- Stretch only until you feel mild tension, not pain.
- Use a chair or wall for balance if necessary.
If you want extra motivation, consider joining group stretching classes.
Group Classes Near You
In addition to daily stretching, group classes combine movement with social interaction, offering even more benefits. Research shows that older adults who take part in community physical activities are 75% less likely to develop functional disabilities.
In Accra and other parts of Ghana, many community centres host morning flexibility sessions and guided stretching classes.
Church Gatherings: Churches across Ghana often include gentle exercise programmes in their weekly schedules, offering a chance to improve physical wellness while connecting with others spiritually.
Dr. Vinci encourages starting small:
“Don’t underestimate the value of small movements. It’s a starting place, and over time, you will gradually achieve greater range.”
These group sessions not only support flexibility but also create opportunities for meaningful social connections, which are key to overall wellbeing.
3. Build Muscle Safely
After improving flexibility with light exercises, it’s time to focus on strengthening your muscles. Building strength not only helps prevent muscle loss but also makes daily tasks – like carrying groceries or climbing stairs – much easier. Starting with a safe routine is key.
Basic Strength Exercises
UnitedHealthcare® highlights the importance of using proper form and progressing gradually when starting strength training.
Below are five beginner-friendly exercises you can try at home:
| Exercise | Instructions | Sets and Reps |
|---|---|---|
| Calf Raises | Stand with feet shoulder-width apart. Rise onto your toes, pause for 1-2 seconds, then lower slowly. | 2-3 sets of 15 reps |
| Wall Angels | Stand with your back against a wall. Slide your arms up and down in a controlled motion. | 2-3 sets of 10-15 reps |
| Chair Squats | Stand in front of a chair. Lower yourself until almost seated, then stand back up. | 2-3 sets of 10-15 reps |
| Wall Push-ups | Place your hands on a wall at shoulder height. Perform push-ups while keeping your body straight. | 2-3 sets of 10-15 reps |
| Plank | Lie on your stomach, place forearms on the floor with elbows under shoulders, and hold your body in a straight line. | 2-3 sets holding for 15-20 seconds |
“Proper form is essential to prevent injuries, especially as you age. Start with lighter weights and focus on learning the correct technique before gradually increasing the load.” – Harper Health
Quick Safety Tips:
- Warm up for 5-10 minutes before starting.
- Take breaks between sessions to allow recovery.
- Stop immediately if you feel sharp pain.
- Keep your breathing steady throughout.
- Use slow, controlled movements to avoid strain.
Home Exercise Equipment
You don’t need fancy gym equipment to get started. Everyday household items can work just as well:
- Water Bottles: Fill 1.5-litre bottles (about 0.4 kg each) for adjustable weights.
- Resistance Bands: These are affordable and available in Accra pharmacies for GH₵30-50. Start with lighter bands, like yellow or red.
- Household Items: Use rice bags (2-5 kg), a sturdy chair for squats, stairs for calf raises, or even a bath towel for resistance exercises.
4. Join Group Activities
Exercising with others can make staying active more fun and help you stick to a routine. Beyond the physical benefits, group activities also help you build social connections, which are essential for your overall well-being as you grow older.
Local Exercise Groups
In Ghana, many community centres, churches, and senior organisations offer fitness sessions tailored for older adults. These might include walking groups, aerobics, water exercises, or chair-based workouts. Check with your local community centre or place of worship to find out what’s available.
If you can’t find a group that suits your needs, why not create one yourself?
Start Your Own Group
Starting your own exercise group is a great way to stay active while bringing people in your community together.
1. Plan Your Programme
Begin with something simple, like a walking group. Pick safe, well-lit routes with even surfaces. Popular spots like the University of Ghana campus or Aburi Botanical Gardens make excellent choices for group walks.
2. Establish Guidelines
Set clear rules so everyone knows what to expect. Decide on meeting times (early mornings are cooler), and set policies for weather and safety. Use tools like WhatsApp to communicate, and figure out what equipment – if any – you’ll need.
3. Build Your Community
Start small, with a few friends or neighbours (5–10 people is a good size). Spread the word by posting flyers at local churches, community centres, clinics, or neighbourhood notice boards. Host a kick-off meeting to agree on a schedule, discuss goals, and decide how to stay in touch.
To keep things interesting, rotate your routes and celebrate milestones together. For added safety and guidance, you might team up with local healthcare providers or fitness experts who can offer professional advice and support.
5. Use Digital Health Tools
Smartphones and apps can play a big role in tracking progress and staying motivated as you age.
Fitness Apps and Devices
Research shows that using mobile health apps can add around 1,100 extra steps daily over 12 weeks. These tools are great for keeping track of your daily activities and reaching fitness goals. For example, DrDoGood’s health management app offers several features to support your health journey:
- Track physical activities
- Set and monitor fitness goals
- Get medication reminders
- Connect with healthcare professionals
- Access health records easily
For those without internet access, DrDoGood also provides basic health services through their USSD code (_920_336#). These tools are a convenient way to stay active and organised.
Mobile Health in Ghana
Digital health tools are becoming an essential part of healthcare in Ghana, making it easier to stay active and manage overall health. With an 80% acceptance rate among seniors using health apps, these tools are clearly making an impact.
Here are a few practical ways to make the most of mobile health tools:
- Daily Activity Tracking: Use apps to monitor steps, distance, and calories burned.
- Goal Setting: Start small, like a 10-minute morning walk, and gradually increase your targets.
- Remote Health Support: Reach out to healthcare providers for virtual consultations when you need advice on exercise or health issues.
“MYHEALTHCOP goes beyond just fitness – they create a wellness ecosystem. The WhatsApp engagement, mobile app, and structured activities make wellness an effortless part of life.”
Studies also reveal that 16% more people engage in regular physical activity when using a mobile app. Plus, about 58% of users say smartphone-based health systems keep them motivated to stick to their routines.
Conclusion: Take The First Step
Starting an active lifestyle can be simple. Even just 5 minutes of physical activity can have positive effects on your health.
Here are a few easy ways to get moving:
- Take a 10-minute brisk walk in your neighbourhood.
- Stand on one foot while holding onto a chair for balance.
- Use resistance bands for basic arm exercises.
Staying active as you age benefits both your body and mind. Dr. Richard J. Hodes, director of NIH’s National Institute on Aging, highlights:
“Even if you haven’t been active previously, it’s important to get started and stay active”.
If you’re unsure where to begin, resources like DrDoGood can help make the process easier. Their offerings include:
- Virtual consultations with healthcare professionals to find exercises that suit you.
- Activity tracking via their mobile app.
- Medication and exercise reminders.
- Connections to local wellness centres.
Before starting any new exercise routine, consult your doctor – especially if you have any pre-existing health conditions – to ensure the activities are safe for you.
“Regular physical activity is important at any age, but especially for older adults. Physical activity keeps muscles, joints, and bones healthy, it also reduces your disease risk, and more.”