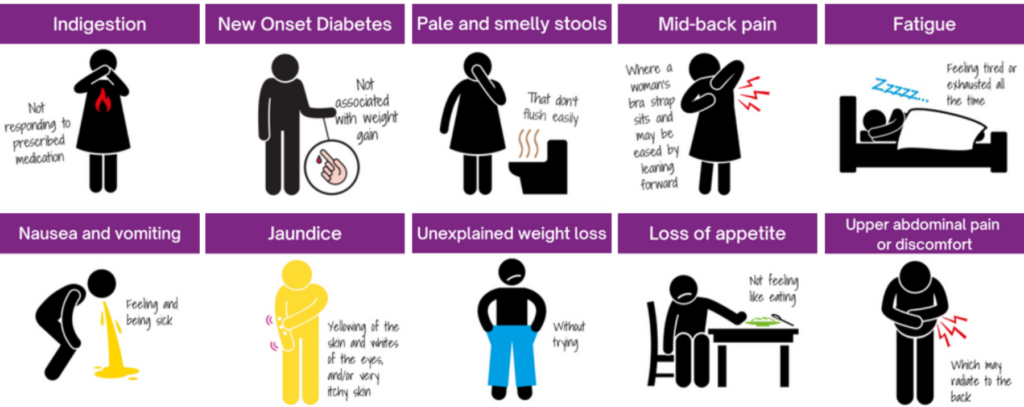
Here’s why you need them:
- Hypertension and diabetes are on the rise in Ghana. Nearly 50% of adults live with hypertension, and many are unaware of their condition.
- Routine visits help catch issues early. Annual screenings for blood pressure, blood sugar, and BMI are essential for preventing severe health problems like stroke and heart disease.
- Vaccinations protect against outbreaks. Stay updated on vaccines like meningitis, flu, and tetanus to avoid preventable illnesses.
- Prenatal care ensures safe pregnancies. Regular check-ups monitor both mother and baby for complications.
- Chronic condition management is critical. Consistent care helps control conditions like hypertension and diabetes, reducing the risks of severe complications.
Quick Tip: Use platforms like DrDoGood to book appointments easily via USSD (*920*336#) or app, starting at GHS 45.
Take action today to stay healthy and avoid unnecessary health risks.
HOW MUCH DOES IT COST TO SEE A DOCTOR IN GHANA? | HEALTHCARE IN GHANA
1. Yearly Health Check-Up
Annual health check-ups are essential for catching potential health issues early. In Ghana, where non-communicable diseases (NCDs) are a leading cause of illness, these check-ups are especially crucial.
The National Health Insurance Authority (NHIA) provides a free annual check-up programme during your birth month. This initiative includes:
- Blood pressure checks
- Blood sugar tests
- Body mass index (BMI) evaluations
- Health counselling
- Referrals for further care
“Health systems worldwide are increasingly recognising the importance of preventive healthcare measures. Early detection and intervention can prevent serious health conditions, reduce the burden of diseases, and improve quality of life. Our free annual health programme is designed with these goals in mind.” – Dr. Dacosta Aboagye, Chief Executive Officer of the NHIA(2024)
Booking your check-up is simple. Through the DrDoGood platform, a basic screening starts at GHS 45. For ongoing care, the Unlimited Consultation Plan is available at GHS 120 per month. These services highlight the importance of regular check-ups in managing and preventing diseases. Considering that NCDs accounted for 74% of global deaths in 2019, early detection in Ghana could be life-saving.
Here’s what you can expect during your annual check-up:
| Screening Type | Purpose | Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| Basic Health Assessment | General health evaluation | Annually |
| Blood Pressure Check | Hypertension screening | Every visit |
| Blood Sugar Test | Diabetes screening | Annually |
| BMI Measurement | Weight management | Every visit |
| Health Counselling | Lifestyle and wellness advice | Annually |
Regular health check-ups are a proactive way to stay ahead of potential health challenges, ensuring a healthier future.
2. Long-Term Health Condition Check-Ups
Keeping chronic conditions like hypertension and diabetes under control means staying on top of regular check-ups. These routine visits aren’t just a formality – they’re essential for managing health effectively.
Studies reveal that only 41.3% of patients with both conditions successfully maintain proper blood pressure levels. This highlights how critical consistent care is for tackling chronic health issues.
During these check-ups, healthcare providers monitor key indicators such as blood glucose, HbA1c levels, blood pressure, heart rate, weight, and even assess whether medications are still suitable. Together, you and your doctor can create a personalised schedule to ensure nothing slips through the cracks.
To make things easier, DrDoGood offers a comprehensive monitoring package for GHS 100 per month. It includes:
- Digital vitals tracking to keep an eye on your key health stats
- Medication reminders so you never miss a dose
- Automated appointment scheduling to stay on track with your care
“Improving glycaemic control can help patients live longer, have an improved quality of life, and delay the development and progression of diabetic complications”.
3. Required Vaccine Appointments
Keeping up with vaccinations is one of the best ways to protect yourself and those around you. Vaccines play a critical role in saving lives across the globe, preventing outbreaks before they even begin.
In Ghana, the introduction of the serogroup A meningococcal conjugate vaccine (MenAfriVac) in 2012 brought a massive reduction in meningitis outbreaks in the northern regions. This is a clear example of how timely immunisation can make a difference.
Here are some key vaccines for adults to consider during your healthcare visits:
| Vaccine Type | Why It Matters |
|---|---|
| Meningitis | Protects against severe complications seen in past outbreaks. |
| Influenza | Shields you from seasonal flu strains that change every year. |
| Tetanus-Diphtheria | Essential for preventing infections, especially after injuries. |
| COVID-19 | Keeps you protected based on the latest treatment guidelines. |
“Historically, immunization is one of the most effective public health interventions, giving millions of children the opportunity to grow up healthy and reach their full potential.” – UNICEF
The importance of vaccination is underscored by the 2015–2016 meningitis outbreak in Northern Ghana. The case-fatality rate for pneumococcal meningitis reached 18.2%, compared to 3.1% for meningococcal meningitis. Such statistics highlight the need for staying up-to-date with your vaccines to avoid severe health risks.
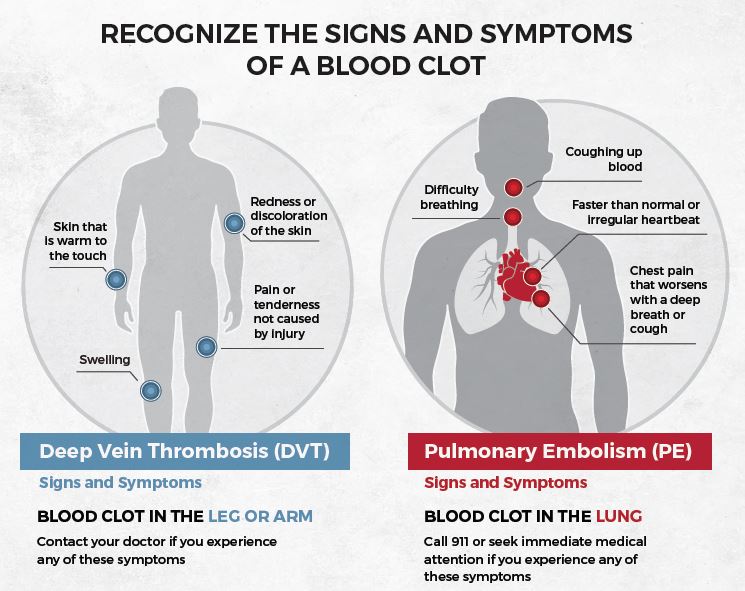
4. Blood Pressure and Blood Sugar Tests
Keeping chronic conditions in check starts with regular and timely testing. In Ghana, where hypertension and diabetes are prevalent, these screenings are particularly crucial. For instance, in 2019, the Ashanti region recorded a hypertension prevalence of 27.3%, with two-thirds of those affected unaware of their condition.
| Test Type | Recommended Frequency | Warning Signs to Watch |
|---|---|---|
| Blood Pressure | Every 6 months, Weekly if you have hypertension or have a family history of hypertension | Headaches, dizziness, shortness of breath |
| Blood Sugar | Annually (or more often if at risk) | Excessive thirst, frequent urination, fatigue |
Shockingly, only 21.8% of Ghanaians living with both hypertension and type 2 diabetes have managed to control both conditions. Regular testing not only offers early warnings but also supports consistent monitoring, which is key to better management.
Why Testing Should Be a Priority
Hypertension is a growing concern, with Africa reporting a pooled prevalence of 57% among older adults – the highest globally. Early detection through regular screening can help prevent life-threatening complications such as:
- Stroke
- Heart failure
- Kidney disease
- Vision problems
Making Testing Easier
Recognising the importance of early detection, accessible testing options are becoming more available. For instance, DrDoGood provides a hassle-free way to book tests at nearby facilities for just GHS 45. They also offer digital tracking for results, automated reminders, and access to expert consultations.
Pair these screenings with your routine check-ups to catch potential issues early. If you’re over 40, have a family history of these conditions, or notice any warning signs, consider scheduling tests more frequently. Early action can make all the difference.
5. Pregnancy Care Check-Ups
Regular prenatal visits are just as important as annual check-ups or managing chronic conditions. They ensure that both you and your baby are monitored closely, helping to catch and address potential issues early.
Prenatal Visit Schedule
| Trimester | Weeks | Visit Frequency | Key Screenings |
|---|---|---|---|
| First Trimester | 8–13 | Initial visit, then usually monthly | Pregnancy confirmation, due date calculation, initial blood tests, and early ultrasound |
| Second Trimester | 14–27 | Typically monthly | Anatomy ultrasound, screening for neural tube defects, glucose test (24–28 weeks) |
| Third Trimester | 28–birth | Every 2 weeks until 36 weeks, then weekly | Monitoring baby’s growth and position, Group B streptococcus testing (affects about 1 in 4 pregnancies) |
First Trimester Priorities
In the first trimester, your healthcare provider will confirm your pregnancy, establish the due date, review your medical history, and conduct essential tests like blood work and an early ultrasound.
Second Trimester Focus
Between weeks 14 and 27, key screenings include an anatomy ultrasound, a test for neural tube defects, and a glucose test to check for gestational diabetes (usually conducted between weeks 24 and 28).
Third Trimester Monitoring
From week 28 until delivery, prenatal visits become more frequent. These appointments focus on:
- Tracking your baby’s growth and position
- Testing for Group B streptococcus, which affects about 1 in 4 pregnancies
“Regular prenatal exams are important both for monitoring your own and your fetus’s health and for giving you and your health professional time to build a working relationship.”
Simplifying Appointment Management
Booking prenatal check-ups doesn’t have to be stressful. With the DrDoGood platform, expectant mothers can:
- Schedule appointments starting at GHS 45
- Receive automated reminders for upcoming visits
- Keep track of all pregnancy-related screenings
- Access virtual consultations when needed
When to Seek Immediate Help
If you experience any of the following symptoms, don’t wait for your next scheduled visit. Contact your healthcare provider right away:
- Severe headaches or vision changes
- Unusual swelling
- Decreased fetal movement
- Vaginal bleeding
For urgent advice or to book an emergency consultation, you can reach out to your healthcare provider through the DrDoGood platform.
How to Book and Track Your Check-Ups
Scheduling your check-ups with DrDoGood is simple and convenient.
Booking Options
DrDoGood provides several ways to book your appointments, tailored to suit different preferences:
| Booking Method | Features | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|
| Mobile App | Complete booking features, appointment reminders, and access to digital health records | Smartphone users |
| Website | Full scheduling tools, including virtual consultations | Users who prefer using a computer |
| USSD Code (*920*336#) | Quick and easy appointment booking without the internet | Individuals without internet access |
Flexible Payment Options
Pick a payment plan that works best for you:
- Pay-As-You-Go: Starting at GHS 45 per consultation.
- Monthly Subscription: Enjoy unlimited consultations for GHS 120 per month.
Managing Your Appointments
DrDoGood makes it easy to stay on top of your healthcare with these helpful features:
- Sync your appointments directly with your phone’s calendar.
- Get automated reminders for upcoming check-ups and medication schedules.
- Access virtual consultations, which include video calls, secure messaging, digital prescriptions, and follow-up coordination.
Employer-Sponsored Benefits
If your employer provides healthcare benefits, you can enjoy additional perks to streamline your healthcare experience. These include:
- Upgraded subscription options starting at GHS 100 per month.
- Access to wellness programmes designed to improve overall health.
- Tools for tracking your health metrics.
- Priority scheduling for specialist appointments.
For urgent support or to schedule your next check-up, reach out to DrDoGood’s support team at +233 50-592-9685.
Next Steps
It’s time to take charge of your health. Here’s how you can get started:
Set Up Your Health Profile
Begin by creating your personalised health profile on the DrDoGood app. Simply download the app and complete your profile to tailor your care experience.
Schedule Your Priority Check-ups
Make sure you’re up to date with your health check-ups. Here’s a quick guide:
| Check-up Type | When to Schedule |
|---|---|
| Annual Health Check | If it’s been more than 12 months since your last visit |
| Chronic Condition Review | Every 3–6 months, as recommended by your doctor |
| Vaccination Updates | As per your immunisation schedule |
| Blood Pressure/Sugar Tests | At least every 6 months |
| Pregnancy Care | As soon as pregnancy is confirmed |
DrDoGood’s digital tools can help you stay on top of these appointments effortlessly.
Use Available Tools
Take advantage of DrDoGood’s handy features to simplify your healthcare journey:
- Automated appointment reminders to keep you on track.
- Digital health records are accessible anytime, anywhere.
- Virtual consultations starting at just GHS 45.
These tools are designed to make managing your health easier and more convenient.
Get Support
Need help? DrDoGood’s support team is here for you. They can assist with:
- Connecting you to the right healthcare provider.
- Explaining your payment options.
- Setting up appointment reminders.
- Managing your digital health records.
Don’t hesitate to reach out for guidance – your health is worth it!
FAQs
Why are regular check-ups for hypertension and diabetes essential in Ghana?
Regular health check-ups for hypertension and diabetes are crucial in Ghana, as these conditions are major contributors to severe health problems such as heart disease, kidney failure, and stroke. By catching these conditions early through routine visits, individuals can manage them effectively, lowering the risk of complications and improving their overall well-being.
A significant concern in Ghana is that many people with hypertension or diabetes are unaware they have these conditions, and treatment rates remain worryingly low. Regular screenings play a key role in ensuring timely diagnosis and access to proper care, leading to better health outcomes. With the rising number of cases in the country, making these check-ups a priority has never been more important.
How can I keep track of my vaccinations, and why is it important for preventing disease outbreaks?
To keep your vaccinations on track, follow the immunisation schedule recommended by healthcare authorities in Ghana. This schedule specifies which vaccines you need and the right time to get them, ensuring you’re protected throughout every stage of life.
Staying current with your vaccinations is crucial for preventing the spread of infectious diseases. When more people are vaccinated, it creates a protective shield for the entire community, especially for those who can’t receive vaccines due to medical conditions. By getting vaccinated on time, you not only protect your own health but also contribute to building a healthier Ghana for all.
How can the DrDoGood platform help me easily manage my health check-ups and appointments?
DrDoGood simplifies taking charge of your health by linking you with reliable healthcare providers through an intuitive web and mobile platform. Whether it’s scheduling your annual check-ups, managing chronic conditions, or booking screenings for hypertension and diabetes, the process is straightforward and hassle-free.
The platform is especially helpful for those with packed schedules, ensuring you keep up with essential appointments and stay on top of your health. Beyond convenience, DrDoGood plays a crucial role in reaching underserved communities across Ghana, making quality healthcare easier to access for everyone.