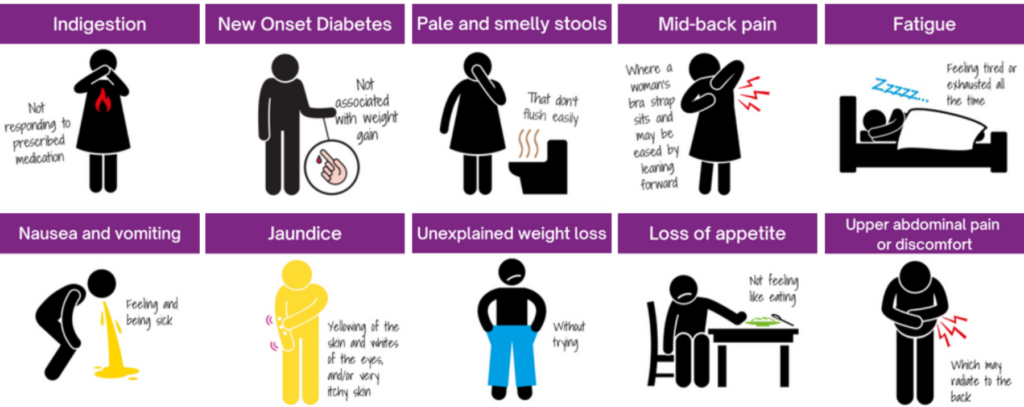
Over 4.16 million Ghanaians live with type 2 diabetes, and women face higher risks due to lifestyle, cultural, and socioeconomic factors. Here’s what you need to know:
- Types of Diabetes in Ghana: Type 1 (affects children), Type 2 (90% of cases, linked to lifestyle), and Gestational Diabetes (10% of pregnancies).
- Key Risk Factors for Women:
- Low physical activity: 82% of women in areas like Ga Mashie don’t meet exercise recommendations.
- Diet: High reliance on starchy staples and processed foods increases risks.
- Pregnancy-related risks: Conditions like preeclampsia and use of oral contraceptives raise the chances of gestational diabetes.
- Mental health: 31% of diabetic patients experience depression.
- Regional Prevalence: Urban areas like Greater Accra (8.2%) have higher diabetes rates than rural areas (1.5%).
- Healthcare Costs: Managing diabetes costs about USD 547 (GH₵6,564) annually, while Ghana’s per capita health expenditure was only GH₵53.5 in 2022.
How to Reduce Your Risk of Diabetes:
- Better Diet Choices: Switch to high-fibre foods (e.g., brown rice, garden eggs) and reduce processed food intake.
- Exercise: Aim for 150–300 minutes of moderate activity weekly.
- Routine Health Checks: Regular blood sugar tests (e.g., FBS, RBS) can help with early detection.
- Support Tools: Platforms like DrDoGood offer affordable virtual consultations, health tracking tools, and personalized care.
Take action today: Stay active, eat mindfully, and schedule regular health checks to reduce your diabetes risk.
Diabetes Statistics for Women in Ghana
Current Numbers and Statistics
Recent studies show that diabetes prevalence in Ghana ranges between 2.80% and 3.95%, with some regions reporting alarmingly high rates. The Western Region leads with a prevalence of 39.80% among adults aged 18 and above, followed by the Ashanti Region at 25.20% and the Central Region at 24.60%.
Urban areas consistently report higher diabetes rates compared to rural areas. For instance, in Ga Mashie, located in the Greater Accra Region, 8.2% of residents aged 25 and above have diabetes. Women in this area are 2.66 times more likely to develop the condition than men. Additionally, adults aged 50 and above show a stark contrast in diabetes prevalence: 6.2% in urban areas versus 2.3% in rural areas.
| Region | Urban Prevalence | Rural Prevalence |
|---|---|---|
| National | 4.7% | 1.5% |
| Ashanti Region | 8.8% | 3.6% |
| Greater Accra | 8.2% | Not reported |
These statistics highlight the importance of examining how women’s specific health behaviours and societal influences contribute to the rising diabetes risk.
Women-Specific Health Factors
Several lifestyle and cultural factors put Ghanaian women at greater risk of developing diabetes. Research conducted in Ga Mashie confirms that women face disproportionately higher risks due to these unique circumstances.
A major factor is low physical activity levels. In Ga Mashie, 82% of women fail to meet recommended exercise levels, compared to 57% of men. This disparity is partly influenced by cultural norms. In Ghana, higher body weight is often associated with prosperity and good health, which can shape dietary habits and attitudes toward weight management.
Mental health also plays a critical role. A 2018 study in Greater Accra revealed that 31% of diabetic patients experience depression. This underscores the need for healthcare approaches that address both physical and mental health challenges, especially for women.
Main Risk Factors
Medical and Pregnancy Risks
In Ghana, certain medical conditions and pregnancy-related factors significantly increase the likelihood of diabetes in women. For instance, research indicates that women who experience preeclampsia (a serious pregnancy-specific condition characterized by high blood pressure and signs of organ damage, primarily affecting the kidneys and liver) are 19 times more likely to develop gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM). Additionally, the use of oral contraceptives has been linked to a 13-fold increase in GDM risk. This is thought to be due to elevated levels of oestrogen and progesterone, which can heighten insulin resistance during pregnancy.
Food and Diet Impact
Dietary habits also play a major role in diabetes risk. In Accra, the consumption of ultra-processed foods among low-income adults increased from 21% in 2011 to 29% in 2013. Traditional diets, often centred around high-carbohydrate staples, have been associated with a 54% higher risk of diabetes. Socioeconomic status further influences food choices: wealthier individuals tend to consume more processed foods and meats, while lower-income households rely on staples like plantain and leafy greens. When combined with low physical activity, these dietary patterns further amplify the risk of diabetes.
Exercise and Movement Habits
Physical inactivity is another major contributor. Among Ghanaian adults with Type 2 diabetes, only 21.4% meet recommended physical activity levels, with 67% reporting low activity. The main barriers to regular exercise include:
- Social influence: 60.8%
- Lack of energy: 59.8%
- Lack of willpower: 58.8%
Experts recommend 75–150 minutes of vigorous activity or 150–300 minutes of moderate aerobic activity weekly. Overcoming these barriers, alongside improving diet and ensuring regular medical check-ups, is essential for reducing diabetes risk.
| Barrier Type | Percentage Affected |
|---|---|
| Social influence | 60.8% |
| Lack of energy | 59.8% |
| Lack of willpower | 58.8% |
Steps to Prevent Diabetes
Better Eating Choices
Making thoughtful food choices plays a big role in preventing diabetes. Ghanaian cuisine, when prepared mindfully, offers plenty of healthy options. Asonaba Owusu Aduomi, Herbal Doctor at the Organic Foods and Wellness Centre, highlights this point:
Through mindful selection and preparation of these foods, individuals with diabetes can enjoy the rich flavors of Ghanaian cuisine while effectively managing their condition.
Research backs this up – each increase in Food Variety Score reduces the odds of Type 2 diabetes to 0.81. Here are some simple dietary adjustments to consider:
| Food Type | Replacement/Addition | Health Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Rice | Switch white rice to brown/Ofada rice | Higher fibre, lower glycaemic index |
| Vegetables | Add garden eggs and nkontomire | Low in carbs, packed with nutrients |
| Proteins | Include fish like mackerel and sardines | Supports better insulin sensitivity |
| Snacks | Opt for pumpkin seeds | Helps with blood sugar control |
Pairing better eating habits with regular physical activity can significantly lower the risk of diabetes.
Getting More Exercise
Exercise is another cornerstone of diabetes prevention. Unfortunately, studies show that 60% of individuals with Type 2 diabetes in Kumasi remain physically inactive. The World Health Organization (WHO) recommends the following guidelines:
- Moderate aerobic activity: 150–300 minutes per week
- Vigorous aerobic activity: 75–150 minutes per week
- Strength training: At least twice a week
In Ghana, a home-based exercise programme showed high participation rates among adults managing Type 2 diabetes. Starting small – like taking daily walks – and gradually increasing activity levels can make a big difference.
Regular physical activity works hand-in-hand with routine health screenings to create a proactive approach to diabetes prevention.
Health Tests and Monitoring
Routine health checks are crucial, especially since less than 25% of Ghanaians with diabetes are aware of their condition. Key tests to consider include:
- Fasting Blood Sugar (FBS)
- Random Blood Sugar (RBS)
- HbA1c testing
The Diabetes Support Center at Holy Family Hospital in Nkawkaw offers affordable screening services. However, as Oluwaseun Ishola, regional manager at Novo Nordisk, explains, accessing care can be challenging for many:
Living on $300 per month for housing, food, transportation and childcare is very tight and poses challenges for people in the income bracket living with diabetes. A lot of times, people with diabetes have to travel considerable distances to multiple locations to access care from the doctor, get test results from the laboratory and then another location to pick up their insulin.
To make screenings and monitoring easier, platforms like DrDoGood provide convenient booking for diabetes tests and ongoing care. With a network of over 43 facilities, they offer personalized chronic care management, simplifying the process for those in need. You can also record your FBS, RBS, and HBA1C on DrDoGood so that you and your healthcare provider can monitor your progress.
World Diabetes Day – AM Show on JoyNews (14-11-17)
Using DrDoGood for Diabetes Care
DrDoGood combines virtual consultations, health tracking, and lifestyle guidance to provide a well-rounded approach to managing diabetes, tailored specifically for Ghanaian women.
Online Doctor Visits
DrDoGood makes it easy to connect with diabetes specialists through virtual consultations at affordable rates. For instance, consultations with family physicians cost ₵200, while lifestyle experts are available for ₵45 per session.
Users can schedule virtual or in-person appointments, get prescriptions, and receive follow-up care without the hassle of travelling long distances. The platform also offers dedicated care for pregnant women dealing with gestational diabetes – a condition affecting 8.5% of pregnancies. Through DrDoGood, these women can consult with obstetricians and endocrinologists to monitor their condition and adjust treatments as needed. To complement these consultations, the platform provides advanced tools for tracking key health metrics.
Health Tracking Tools
DrDoGood equips users with a suite of tools to monitor essential diabetes-related health indicators, including:
- Blood glucose levels with personalised target ranges
- BMI and waist circumference tracking
- Blood pressure monitoring
- Physical activity logs
- Medication schedules with reminders
These tools empower users to stay on top of their health while incorporating meaningful lifestyle changes.
Diet and Exercise Support
DrDoGood also focuses on lifestyle adjustments by connecting users with registered dietitians who provide nutrition advice rooted in local food traditions. Here’s a snapshot of the services offered:
| Service | Description | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Meal Planning | Custom diet plans using familiar ingredients | Improved blood sugar management |
| Exercise Programs | Home-friendly workouts for all fitness levels | Encourages regular activity |
| Wellness Classes | Access to group activities at partner centres | Builds motivation and consistency |
| Nutritional Guidance | Consultations with dietitians | Expert dietary recommendations |
With a network of 43 facilities and over 200 licensed professionals, DrDoGood ensures that women in Ghana have access to affordable, high-quality diabetes care.
Conclusion
Diabetes among women in Ghana is a pressing issue that calls for immediate attention. Tackling this challenge starts with regular health screenings, adopting healthier eating habits, and staying active. Women who prioritise consistent blood sugar checks and embrace dietary changes – such as incorporating local, nutrient-rich foods like kontomire and garden eggs – can significantly improve their health. These lifestyle adjustments create a strong foundation for professional care to build upon.
To make diabetes care more accessible, DrDoGood connects Ghanaian women to affordable services through a network of 43 facilities and over 200 licensed professionals. With consultations starting at just ₵45, the platform offers virtual visits, personalised progress tracking, and guidance tailored to local diets, ensuring that diabetes prevention is within reach for many.
Addressing diabetes in Ghana requires both individual effort and professional support. Through education, regular health checks, and leveraging technology, women can take proactive steps toward managing their health. The numbers don’t lie – the time to act is now.
FAQs
What cultural factors increase the risk of diabetes among women in Ghana?
Lifestyle Factors Contributing to Diabetes Risk Among Women in Ghana
In Ghana, certain everyday habits and traditional practices can increase the likelihood of diabetes among women. For instance, diets often include high-carbohydrate meals and sugary treats, which, when combined with reduced physical activity – especially in urban areas – can lead to weight gain and other health issues. Additionally, societal norms sometimes discourage women from prioritising their health, making it harder to adopt preventive measures. There’s also the perception that being overweight signifies affluence and good health, which can unintentionally promote unhealthy weight gain.
Reducing this risk requires a shift towards healthier living. Eating balanced meals, staying physically active, and scheduling regular health check-ups are key steps. Platforms like DrDoGood provide valuable support by connecting women with wellness services, offering diet advice, and equipping them with tools to manage chronic conditions like diabetes effectively.
What are some practical ways for women in urban Ghana to manage diabetes-related healthcare costs?
Managing Diabetes-Related Healthcare Costs in Urban Ghana
Dealing with the expenses of diabetes care can be tough, but there are ways for women in urban Ghana to manage costs without compromising their health.
One smart strategy is focusing on prevention and early detection. Regular health check-ups can catch diabetes in its early stages, often avoiding the need for expensive treatments later. Platforms like DrDoGood simplify the process by helping you book affordable consultations and find nearby healthcare facilities that accept your insurance.
Living a healthy lifestyle is another important step. Eating a balanced diet, staying physically active, and managing stress are all effective ways to keep blood sugar levels in check and avoid complications. The DrDoGood app offers resources like professional diet and fitness advice, wellness classes, and tools for managing chronic conditions – all designed to support better health while keeping costs down.
Lastly, if you have access to employer-sponsored health benefits, make the most of them. These benefits can help cut down on out-of-pocket expenses for medications, doctor visits, and wellness programmes.
How does mental health impact diabetes management for women in Ghana, and what steps can be taken to address it?
The Role of Mental Health in Managing Diabetes for Women in Ghana
Mental health is a critical factor in managing diabetes effectively, especially for women in Ghana. Emotional challenges like stress, anxiety, and depression can disrupt efforts to maintain key habits such as eating a balanced diet, exercising regularly, and sticking to prescribed medications – all of which are essential for keeping diabetes under control.
To tackle these challenges, women can explore stress-relief practices such as mindfulness exercises, yoga, or even pursuing hobbies that bring joy and relaxation. Building a strong support system (like we’ve done in this WhatsApp Diabetes community) is equally important. Whether it’s leaning on family and friends or consulting mental health professionals, having a network can ease emotional burdens.
For more structured support, platforms like DrDoGood offer valuable resources. They connect users with licensed therapists and wellness experts, craft personalised care plans, and provide access to wellness facilities. By focusing on both mental and physical well-being, women can take a more balanced approach to managing diabetes effectively.