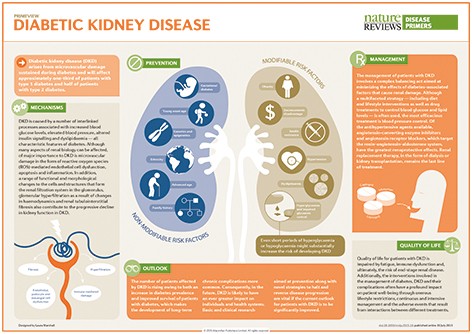
We’ll walk through where chest pain can come from, what it might mean depending on the location and cause, and how symptoms can differ between men, women, and children. You’ll also learn what to do and when to seek help immediately.
Heart Causes Of Chest Pain
These are the most feared causes of chest pain—and for good reason. Heart-related chest pain is often a medical emergency.
1. Angina pectoris:
- This is a warning sign of heart disease. You should speak to a doctor as soon as possible. You can find an expert here
- It feels like pressure or tightness in the chest.
- This chest pain is triggered by physical activity or emotional stress and usually goes away with rest or nitroglycerin.
- You should still speak with a doctor to prevent an actual heart attack from happening.
- You’re at risk if you
- Are a man >45yrs (More common in men) or a woman >55yrs
- Hypertension
- Diabetes
- Smoking
- obese
- poor diet
2. Myocardial infarction (heart attack):

A heart attack, medically called a myocardial infarction (MI), happens when blood flow to a part of the heart is suddenly blocked, causing damage to the heart muscle.
It’s a medical emergency that needs prompt treatment to prevent serious complications or death.
Heart Attack Symptoms
Heart attack symptoms can vary from person to person. Some experience the classic crushing chest pain, while others—especially women, the elderly, or people with diabetes—may have more subtle signs.
Common symptoms include:
- Chest pain or discomfort (tightness, pressure, squeezing, or fullness in the center or left side of the chest almost like there’s something sitting on your chest)
- Pain in the arm, jaw, neck, back, or stomach
- Shortness of breath
- Cold sweat
- Nausea or vomiting
- Lightheadedness or sudden dizziness
- Unusual fatigue, especially in women
If these symptoms last more than a few minutes or keep coming and going, seek emergency care immediately.
Who’s at Risk?
Several factors increase the risk of a heart attack, many of which are lifestyle-related. These include:
- High blood pressure
- High cholesterol (especially high LDL, you need to do a blood test to know your LDL level. You can access that here)
- Smoking
- Diabetes
- Obesity or being overweight
- Physical inactivity
- Unhealthy diet (speak to a dietitian here)
- Stress
- Family history of heart disease
- Age (men over 45, women over 55)
How is a Heart Attack Treated?
Emergency treatment focuses on restoring blood flow to the heart as quickly as possible to limit damage. This includes:
- Medications: such as aspirin, nitroglycerin, clot-busters (thrombolytics), beta-blockers, and blood thinners.
- Procedures: like angioplasty (to open blocked arteries with a balloon and stent) or coronary artery bypass surgery if multiple vessels are involved.
- Hospital care: continuous monitoring, oxygen, and support for complications.
- Aftercare: cardiac rehab, lifestyle changes, and medications to reduce future risk.
Lung Causes of Chest Pain
1. Pulmonary Embolism
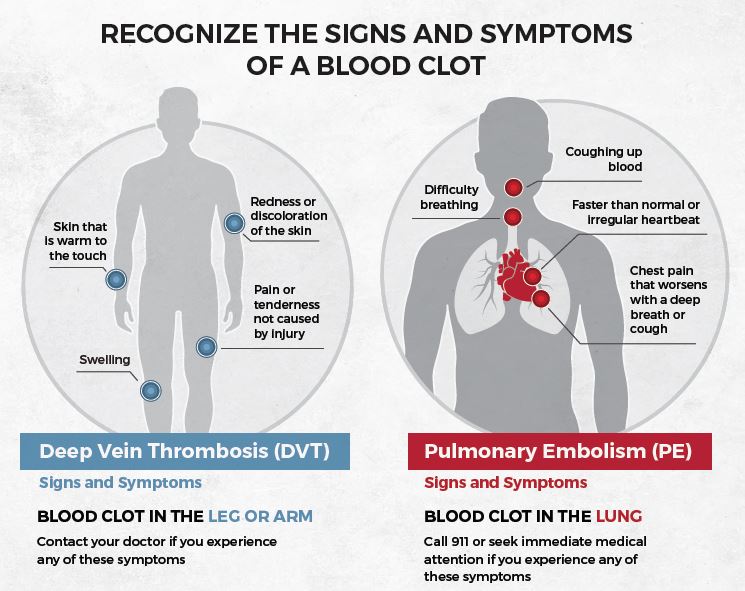
A life-threatening emergency that requires immediate medical attention.
A pulmonary embolism (PE) is a sudden blockage in one of the pulmonary arteries in the lungs, usually caused by a blood clot that travels from the deep veins of the legs (a condition known as deep vein thrombosis, or DVT). This blockage prevents proper blood flow to the lungs, which can reduce oxygen levels in the body and strain the heart.
Symptoms:
- Sudden, sharp chest pain (worse with breathing)
- Shortness of breath
- Fast heart rate (tachycardia)
- Cough, sometimes with blood (hemoptysis)
- Dizziness or fainting
- Anxiety or a sense of doom
- Recent surgery or trauma
This is a medical emergency. See a doctor now if you have of these symptoms.
Risk Factors:
- Prolonged immobility (e.g., long flights, bed rest)
- Pregnancy or recent childbirth
- Use of hormonal contraceptives
- Clotting disorders or a history of deep vein thrombosis (DVT)
Treatment of PE:
Treatment includes anticoagulants (blood thinners) to prevent new clots and help the body dissolve existing ones. In severe cases, clot-busting drugs (thrombolytics) or surgical removal may be needed.
2. Pneumonia
Pneumonia is a lung infection that makes it hard to breathe. It happens when germs like bacteria, viruses, or fungi get into your lungs and cause the small air spaces (called air sacs) to fill with fluid or pus.
Symptoms:
- Dull, aching chest pain (worse with breathing or coughing)
- Fever, chills
- Cough with phlegm or mucus
- Fatigue
- Shortness of breath
- Loss of appetite
Risk Factors:
- Age extremes (infants, elderly)
- Chronic illnesses (e.g., diabetes, heart failure, asthma)
- Smoking
- Recent respiratory infection
- Weakened immune system (e.g., HIV, chemotherapy)
Treatment of Pneumonia :
- Bacterial pneumonia: Antibiotics
- Viral pneumonia: Supportive care (antivirals in some cases)
- Fungal pneumonia: Antifungal medications
Hospitalization may be required in severe cases, especially in older adults or those with comorbidities.
Gastrointestinal Causes of Chest Pain
Not all chest pain comes from the heart—sometimes, it starts in your digestive system. These types of chest pain are often confused with heart-related problems but tend to feel burning, gnawing, or cramping rather than tight or pressure-like. Here are three common culprits:
1. Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
Also known as acid reflux, GERD occurs when stomach acid backs up into the esophagus.
Symptoms:
- Burning sensation behind the chest bone (“heartburn”)
- Pain that worsens after eating or when lying down
- Sour taste in the mouth or acid regurgitation
- Hoarseness, chronic cough, or sore throat
Risk Factors:
- Obesity
- Smoking
- Pregnancy
- Eating large or fatty meals
- Lying down soon after eating
- Certain medications (e.g., NSAIDs, calcium channel blockers)
Treatment of GERD:
GERD is managed with lifestyle changes (eating smaller meals, avoiding late-night eating, elevating the head of the bed), antacids, and acid-reducing medications like proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) or H2 blockers. In chronic cases, surgery may be considered.
2. Peptic Ulcers
Ulcers are sores in the stomach or upper part of the small intestine caused by acid erosion.(Read More about this here)
Symptoms:
- Dull or burning pain in the upper abdomen or lower chest
- Pain that improves or worsens with food (depending on ulcer location)
- Bloating, burping, nausea
- In severe cases: vomiting blood or black stools
Risk Factors:
- Infection with Helicobacter pylori bacteria
- Long-term use of NSAIDs (e.g., ibuprofen, aspirin)
- Smoking
- Excessive alcohol intake
- Stress (can worsen symptoms but not a direct cause)
Treatment of PUDx:
Peptic ulcers are usually treated with a combination of antibiotics (if H. pylori is present), acid-reducing medications, and lifestyle changes. Avoiding NSAIDs and smoking is crucial to healing.
3. Gallstones (Cholelithiasis)
Gallstones are hardened deposits that form in the gallbladder and can block bile flow.
Symptoms:
- Sudden, intense pain in the right upper abdomen that may radiate to the chest, shoulder, or back
- Pain often triggered by fatty meals
- Nausea or vomiting
- Bloating or indigestion
Risk Factors:
- Female gender
- Age over 40
- Obesity or rapid weight loss
- Pregnancy
- High-fat, low-fiber diet
- Family history of gallstones
Treatment of Gallstones:
Gallstones that cause symptoms are typically treated with surgical removal of the gallbladder (cholecystectomy). In some cases, medications may be used to dissolve stones, but this is less common. Dietary changes can help prevent flare-ups before surgery.
Musculoskeletal Causes of Chest Pain
Musculoskeletal chest pain originates from the muscles, bones, or connective tissues of the chest wall. Unlike heart or lung-related pain, this type of chest discomfort is often localized, tender to touch, and can worsen with movement or deep breathing. Though not life-threatening, it can be quite distressing. Here are two of the most common causes:
1. Costochondritis
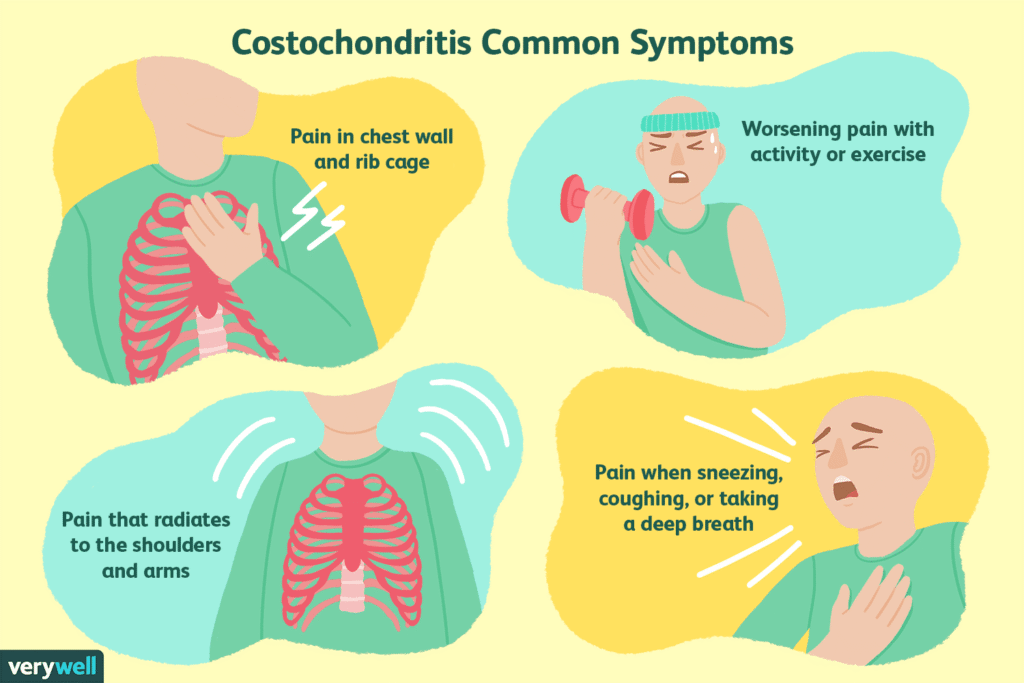
An inflammation of the cartilage that connects the ribs to the breastbone (sternum).
Symptoms:
- Sharp or aching pain in the front of the chest (usually on one side)
- Pain that worsens with movement, deep breaths, or coughing
- Tenderness when pressing over the affected rib joints
- Pain that can mimic a heart attack but is not related to the heart
Risk Factors:
- Physical strain (e.g., heavy lifting, strenuous exercise)
- Upper respiratory infections (due to persistent coughing)
- Injury or trauma to the chest wall
- Repetitive motion or poor posture
Treatment of costochondritis:
Costochondritis usually improves on its own. Treatment includes:
- Pain relief with NSAIDs like ibuprofen or naproxen
- Warm compresses or ice packs to reduce inflammation
- Stretching and posture correction
- Rest and avoiding activities that trigger pain
- Persistent or severe cases may require corticosteroid injections.
2. Muscle Strain & Rib Fractures
These occur from overuse, trauma, or direct injury to the chest wall.
Symptoms:
- Localized chest pain that worsens with movement, deep breathing, or coughing
- Bruising or swelling over the injured area (especially in fractures)
- Pain during certain motions (like lifting, twisting, or stretching)
- In rib fractures: a crackling or popping sensation, or visible deformity
Risk Factors:
- Direct trauma (falls, car accidents, sports injuries)
- Repetitive physical activity (e.g., rowing, heavy lifting)
- Severe coughing (can strain intercostal muscles or even cause fractures)
- Bone-weakening conditions like osteoporosis (for fractures)
Treatment:
- Rest and activity modification to allow healing
- NSAIDs or acetaminophen for pain management
- Cold compresses in the first 48 hours; later warm compresses may help
- In rib fractures: no tight bandaging (to prevent breathing issues), but pain control is essential to avoid lung complications like pneumonia
- Physical therapy or breathing exercises may be recommended during recovery
If you can pinpoint your chest pain with one finger or it worsens when you press on it, it’s likely musculoskeletal, not cardiac—but always consult a doctor if you’re unsure.
Psychological Causes of Chest Pain
Sometimes, chest pain starts in the mind. Psychological stress can trigger real, physical symptoms that mimic serious medical conditions. The chest pain from panic or anxiety is typically tight, burning, or stabbing, and can feel overwhelming. Here are two common psychological causes:
1. Panic Attacks

A panic attack is a sudden episode of intense fear that triggers severe physical reactions when there is no real danger.
Symptoms:
- Sudden, sharp or crushing chest pain
- Palpitations (rapid or pounding heartbeat)
- Shortness of breath or a choking sensation
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
- Sweating, chills, or hot flashes
- Tingling in the hands or feet
- An intense fear of dying
- Usually peaks within 10–15 minutes and then fades
Risk Factors:
- High stress levels
- Past trauma or abuse
- Family history of anxiety or panic disorders
- Certain medical conditions (e.g., hyperthyroidism)
- Stimulants (e.g., caffeine, cocaine)
Treatment:
- Reassurance and breathing techniques to calm the nervous system
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) to address the root cause of panic from a trained psychologist here.
- Medications, such as SSRIs or benzodiazepines (for short-term use)
- Lifestyle modifications: reducing caffeine, getting enough sleep, regular exercise, and mindfulness practices
2. Anxiety Disorders
Generalized anxiety or chronic stress can cause a constant feeling of tension, often manifesting physically in the chest.
Symptoms:
- Persistent chest tightness or discomfort (not sharp or stabbing)
- A feeling of a heavy weight on the chest
- Increased heart rate
- Fatigue or restlessness
- Difficulty concentrating or sleeping
- Tension in the neck, shoulders, and back
- Often worse at rest or in quiet moments
Risk Factors:
- Chronic stress (work, relationships, finances)
- Perfectionism or people-pleasing tendencies
- Underlying health issues or chronic pain
- Substance use or withdrawal
- Poor sleep and lack of routine
- Therapy, especially CBT, helps patients reframe negative thought patterns
Treatment Summary:
- Medications like SSRIs or SNRIs may be prescribed for long-term anxiety
- Mindfulness, journaling, regular physical activity, and good sleep hygiene are key self-care strategies
- Breathing exercises and progressive muscle relaxation can help in the moment
Diagnostic Approach to Chest Pain
Because the causes of chest pain vary, you can expect to do some of these when you speak to your doctor or visit a Hospital.
- History Taking – Questions about the pain’s nature, triggers, and associated symptoms.
- Physical Examination – Including vital signs and listening to the chest.
- ECG – Detects heart attacks or rhythm problems.
- Blood Tests – Especially troponins, which indicate heart muscle damage.
- Chest X-ray – Useful for lung-related issues or heart enlargement.
- Echocardiogram – Assesses heart function via ultrasound.
- Stress Testing or CT Angiography – Evaluates heart blood flow and blockages.
- Endoscopy or Abdominal Ultrasound – If gastrointestinal causes are suspected.
Preventing Chest Pain
While some causes of chest pain are unavoidable, many can be prevented:
Heart Health
- Eat a heart-friendly diet (low salt, low saturated fat)
- Exercise regularly
- Avoid smoking
- Manage stress effectively
- Keep chronic illnesses like diabetes and high BP under control
Gastrointestinal Care
- Avoid spicy and fatty meals
- Eat slowly and in small portions
- Don’t lie down right after eating
Muscle and Bone Health
- Warm up before exercise
- Use ergonomic support at work
- Treat injuries promptly
Mental Health
- Practice relaxation techniques
- Seek help for anxiety and depression
- Avoid overworking and burnout
Conclusion
Chest pain is your body’s way of saying something might be wrong. It can be minor, but it can also be serious. Whether you’re a woman with vague discomfort,or a man with pressure in your chest, the rule is the same: don’t ignore it.
When in doubt—check it out. It could save your life.